LV: Left Ventricle – Definition
The left ventricle (LV) is the thick-walled, cone-shaped chamber of the heart responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood into the systemic circulation via the aorta. Positioned at the bottom left of the heart, it receives blood from the left atrium through the mitral valve, then contracts forcefully to generate the high pressures necessary to propel blood through the arteries to all organs and tissues. Its muscular wall is significantly thicker than that of the right ventricle because it must overcome greater resistance in the systemic circulation compared with the low-pressure pulmonary circuit.
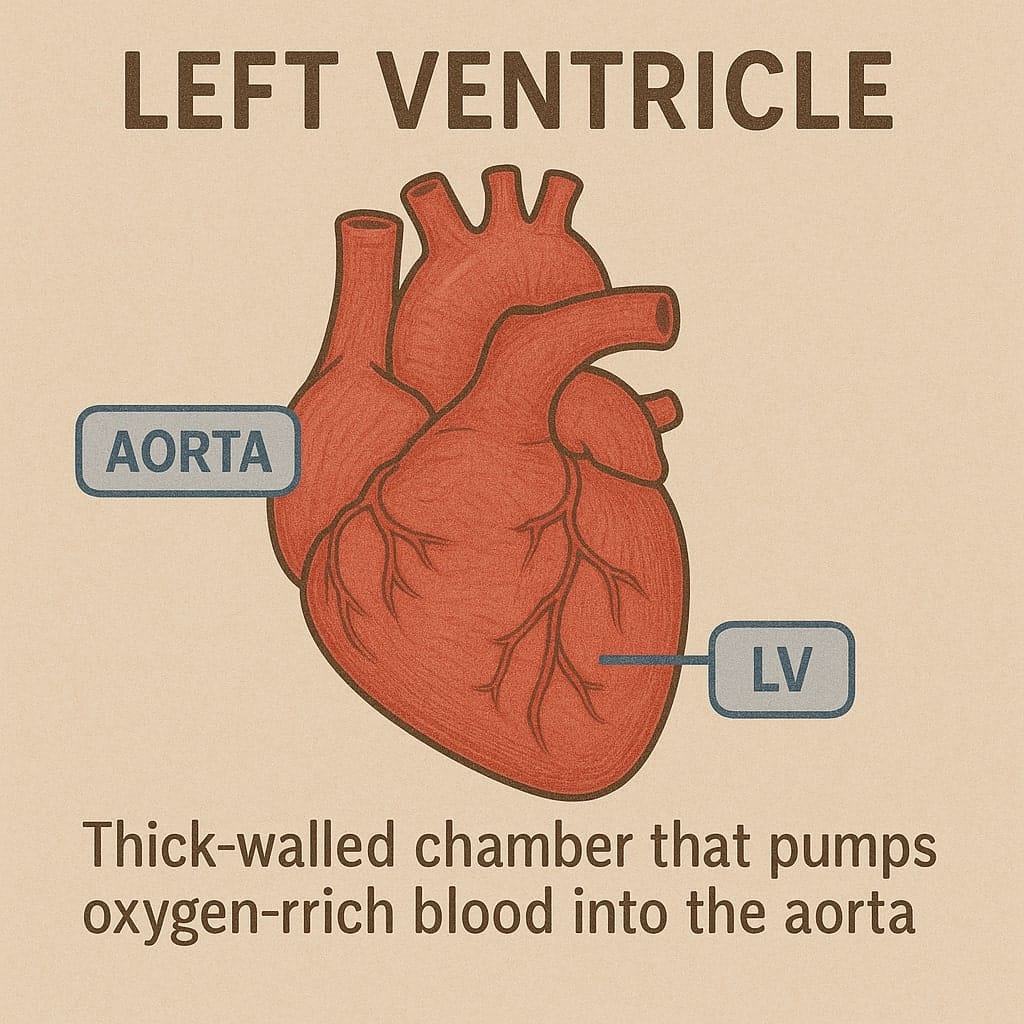
Function of the left ventricle is assessed by measurements such as ejection fraction (percentage of blood ejected each beat) and stroke volume, often obtained via echocardiography, MRI or nuclear imaging. Conditions affecting the LV include hypertrophy due to hypertension or valvular disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, ischemia leading to infarction, and heart failure when pumping capacity declines. Management ranges from lifestyle modifications and medications (ACE inhibitors, beta blockers) to device therapy (pacemakers, implantable defibrillators) and, in severe cases, mechanical support devices or transplantation. Maintaining healthy LV function is essential for adequate systemic perfusion and overall cardiovascular health.
Our Store Supports Our Blog, Thank you For Shopping!
Best selling products
New Valve New Vibes Heart Valve Replacement Sweatshirt
Price range: $25.50 through $31.00Stronger With Every Beat Heart Surgery Sweatshirt
Price range: $25.50 through $31.00Heart Warrior Support Team Sweatshirt
Price range: $25.50 through $31.00New Valve New Vibes Heart Valve Replacement
Price range: $20.00 through $22.00Stronger With Every Beat Heart Surgery
Price range: $20.00 through $22.00







